M-Locus (Merle)
Turnaround: approx. 2 weeks
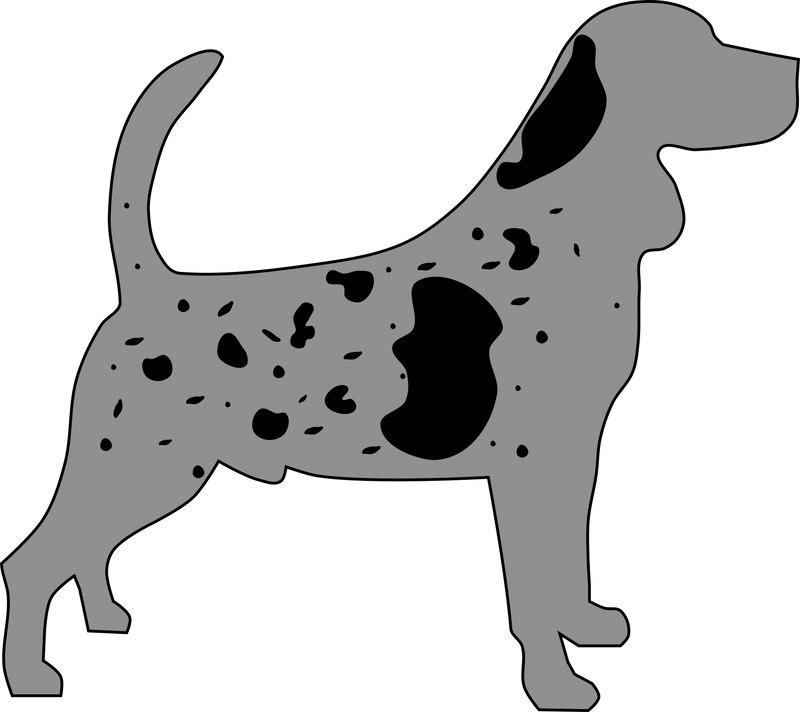
The M-Locus controls Merle colouring, which is a dominant trait. For some breeds such as Shetland Sheepdog, Australian Shepherd, Cardigan Welsh Corgi and Dachshund, Merle is considered one of the standard colours.
There are two types of pigment in dog coat colours, eumelanin and pheomelanin. In Merle dogs, a dilution of the eumelanin pigment occurs in a variable pattern from very pale grey to dark grey and can darken as the dog gets older.
The Merle test checks for an insertion of DNA sequence (SINE insertion) in the SILV gene. A dog who is heterozygous for this insertion (one copy of Merle) will show the Merle colouring. Dogs who are homozygous for the insertion of DNA (two copies of Merle) are known as "double Merle" and this genotype is associated with many health issues, including deafness and eye abnormalities. Recent research has shown that the prevalence of deafness in Merle dogs is 54.6% in double merles and 36.8% in single merles.
A dog who has one copy of the insertion can also show very little Merle colouring and is described as a cryptic merle. Genetic testing is recommended to prevent the breeding of two merle dogs and the production of double merle puppies.
Scientific references:
Clark et al., (2006) Retrotransposon insertion in SILV is responsible for merle patterning of the domestic dog. PNAS, 103 (5) 1376-1381